The Bat Nebula is a region of ionized gas within the larger Veil Nebula, an ancient supernova remnant located in the constellation Cygnus (the Swan). It is listed as IC 1340 in the Index Catalogue.
The celestial Bat is part of the Eastern Veil Nebula (Caldwell 33), which also includes the bright regions NGC 6995 and NGC 6992. Together, NGC 6995 and NGC 6992 are known as the Network Nebula. The Bat Nebula appears in the southern portion of the Eastern Veil, between NGC 6995 and the Southeastern Knot.
The Eastern Veil, Western Veil, and Fleming’s Triangle (Pickering’s Triangle) are the three visual components of the Veil Nebula, a large cloud of ionized gas and dust that stretches across an area with a radius of six full Moons.
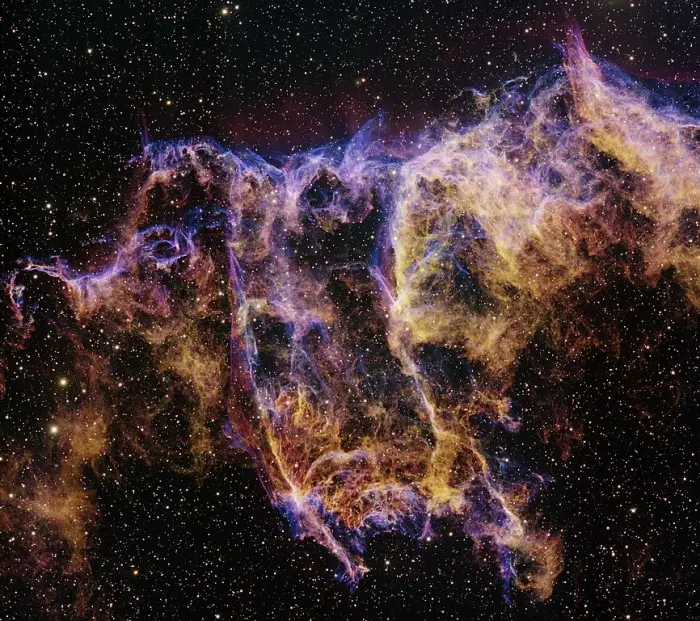

This image was obtained with the wide-field view of the Mosaic camera on the Mayall 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. IC 1340 is part of a large supernova remnant called the Cygnus Loop. Image (rotated from original): T.A. Rector (University of Alaska Anchorage) and H. Schweiker (WIYN and NOIRLab/NSF/AURA) (CC BY 4.0)
The Veil Nebula constitutes the visible portion of the Cygnus Loop, the remnant of a supernova produced by a star with 20 times the Sun’s mass between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. The supernova remnant has since expanded to a size about 3 degrees across. It expands at a velocity of around 1.5 kilometres per hour.
The Bat Nebula was discovered by the American astronomer Truman Henry Safford on September 12, 1866. Safford made his observations at the Dearborn Observatory in Illinois between 1866 and 1868. He published his list of nebulae in 1887 as an appendix to the Dearborn Observatory Report.
The Bat Nebula was discovered much later than some of the brighter portions of the Veil Nebula. The Western Veil Nebula (Caldwell 34, NGC 6960) was first reported by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel on September 7, 1784. It is popularly known as the Witch’s Broom, Filamentary Nebula, or Lacework Nebula. It appears near the magnitude 4.22 yellow giant 52 Cygni. The Witch’s Broom is a popular target for amateur astronomers and astrophotographers because it is the easiest part of the Veil Nebula to find.
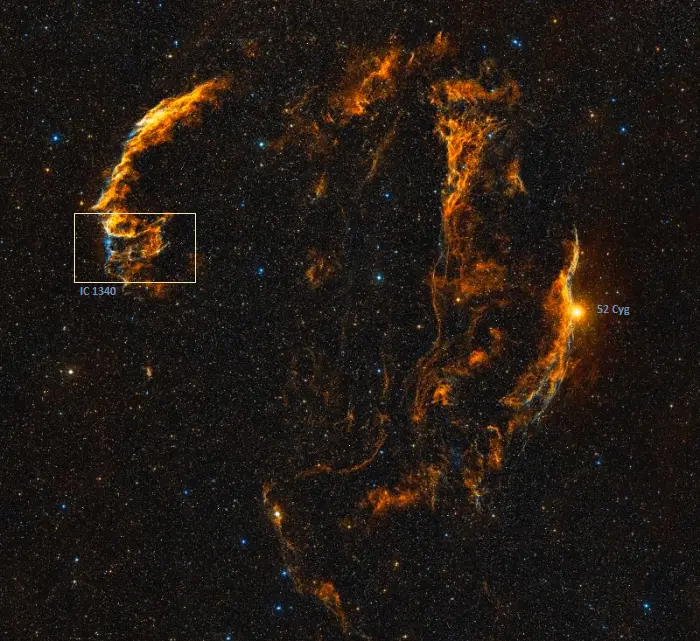

IC 1340 in the Veil Nebula, image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
The Eastern Veil Nebula (Caldwell 33) was discovered by the English astronomer John Herschel (son of William Herschel) on September 7, 1825.
The Veil Nebula appears in the region between Aljanah (Epsilon Cygni) and Zeta Cygni at one of the Swan’s wings. It can be found using the bright stars of the Northern Cross, a prominent asterism formed by the brightest stars of Cygnus.
The Bat Nebula lies near the centre of the triangle formed by Aljanah, Zeta Cygni and 52 Cygni.
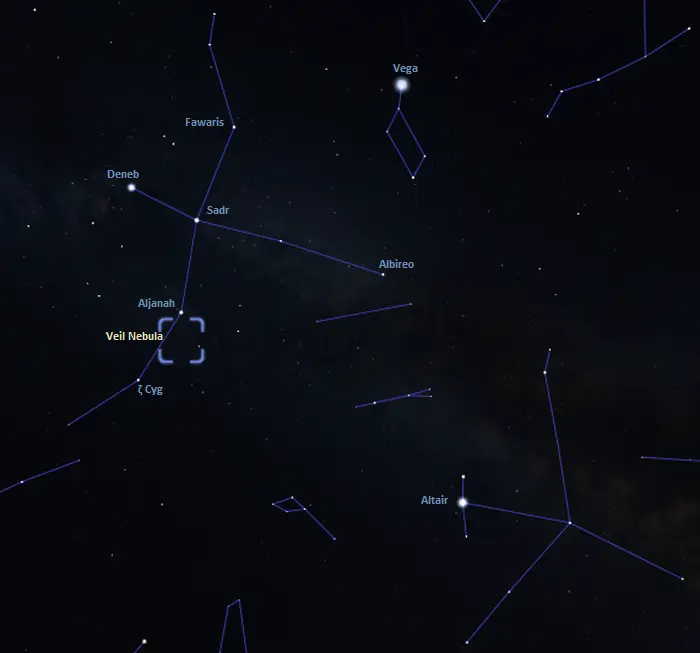
The location of the Veil Nebula, image: Stellarium
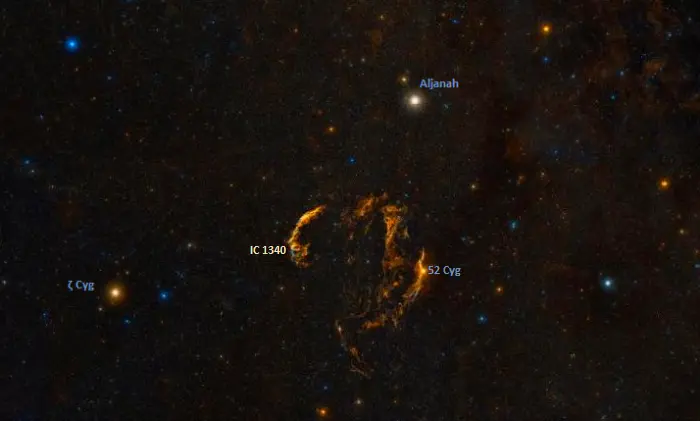

The location of the Bat Nebula (IC 1340), image: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
The best time of the year to observe the Bat Nebula and other deep sky objects in Cygnus is during the month of September, when the Swan constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening.