The Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula located 5,500 – 7,500 light-years away in the equatorial constellation of Eridanus (the River). It has an apparent magnitude of 10.5 and an apparent size of 0.650 by 0.611 arcminutes. The nebula has the designation NGC 1535 in the New General Catalogue.
Like all planetary nebulae, NGC 1535 formed when a star similar to the Sun reached the end of its life and expelled its outer layers into space. Now, the hot stellar remnant illuminates the expanding clouds of ejected material, making them glow as a bright, complex nebula. The layers of expelled gas will eventually dissipate into the interstellar medium and the central star will cool and become a white dwarf.
The central star of NGC 1535 is an O-type star of the spectral type O(H)5. It is listed as HD 26847 in the Henry Draper Catalogue (HD). The star is believed to have a gravitationally bound companion.
Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula looks similar to the nebula NGC 2392 in the constellation Gemini. Both nebulae have a brighter inner region and a fainter outer halo. The inner shell of Cleopatra’s Eye expands at 21 km/s and the outer at 7.5 km/s.
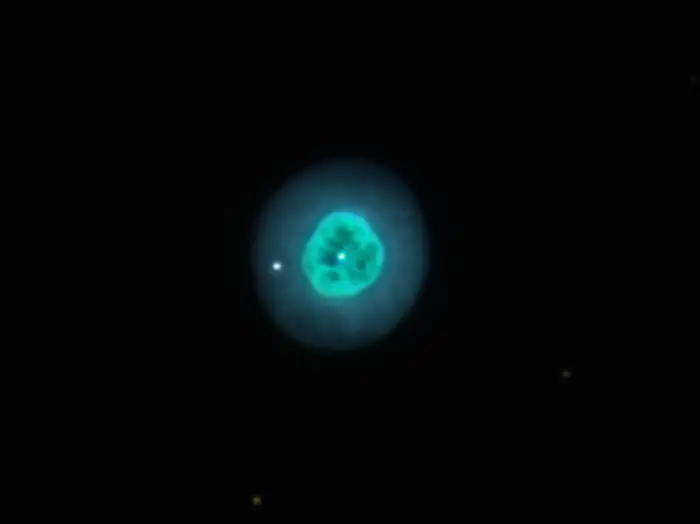
Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula (NGC 1535), image credit: Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona (CC BY-SA 3.0 US)
Facts
Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula was discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7-inch reflector on February 1, 1785. Herschel catalogued the object as IV 26, describing it as “very bright, perfectly round or very little elliptical, planetary but ill defined disk.” He believed it to be a very compressed star cluster located at a large distance.
His son John Herschel listed the object as GC 826 in his General Catalogue and classified it as a globular cluster.
The Danish astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer, who compiled the New General Catalogue based on Herschel’s observations, listed the object as NGC 1535, classifying it as a planetary nebula.
Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula can be observed in amateur telescopes and is included in the Herschel 400 catalogue. Like other deep sky objects on the Herschel 400 observing list, it can be spotted in a 6-inch or larger telescope and is visible from the mid-northern latitudes.
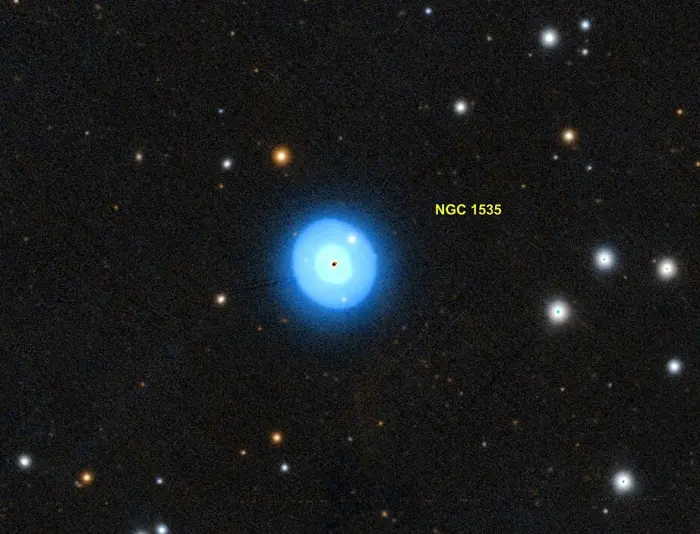

NGC 1535, image created using the Aladin Sky Atlas software from the Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center and
Pan-STARRS (Panoramic Survey Telescope And Rapid Response System), credit: Donald Pelletier (CC BY-SA 4.0)
Location
The Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula appears in the northern part of the constellation Eridanus (the River), near the magnitude 2.95 star Zaurak (Gamma Eridani). The nebula can be found near the imaginary line connecting Zaurak and the bright Rigel (Beta Orionis) in Orion, at the point where this line intersects with the one extended from Arneb (Alpha Leporis) in Lepus to Rana (Delta Eridani) in Eridanus.
The Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula is best observed in 10-inch or larger telescopes, which reveal its fuzzy disk and some of the darker features around the bright central star. Larger instruments will show the nebula’s two-shell structure.
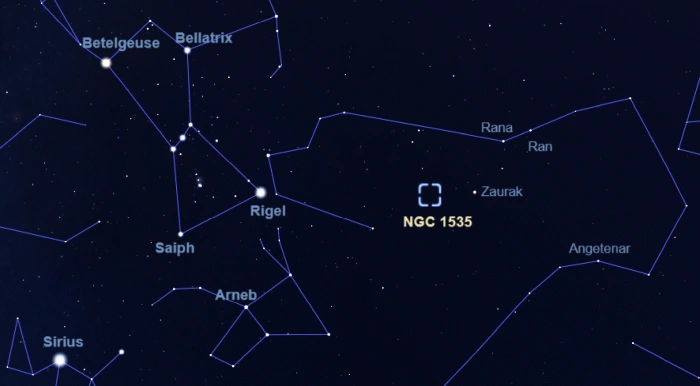
The location of Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula (NGC 1535), image: Stellarium
At declination -12° 44’, NGC 1535 is visible from virtually anywhere on Earth for at least part of the year. The best time of the year to observe it is during the month of December, when the constellation Eridanus appears higher above the horizon in the early evening.
Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula – NGC 1535
| Constellation | Eridanus |
| Object type | Planetary nebula |
| Right ascension | 04h 14m 15.7689913368s |
| Declination | −12° 44′ 21.932484324″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 10.5 |
| Apparent size | 0.650′ × 0.611′ |
| Distance | 5,500 – 7,500 light-years (1,740 – 2,310 parsecs) |
| Names and designations | Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula, NGC 1535, PN G 206.4-40.5, PK 206-40.1, PN G206.4-40.5, PN ARO 22, VV 19, VV’ 25, dML87 112, IRAS 04119-1251, 2MASX J04141578-1244216, 2MASS J04141576-1244219, UITBOC 627, VERA J0414-1244, HD 26847, GCRV 2426, BD-13 842, GALEX J041415.7-124422, GALEX J041415.7-124423, GLEAM J041415-124423, GSC 05318-00563, GSC2 S0211101304, NVSS J041415-124422, PMN J0414-1244, PSCz P04119-1251, SCM 2, TD1 31084, SPASS J041413-124427, TIC 332705938, WEB 3770, uvby98 100026847, GEN# +1.00026847, TYC 5318-563-1, Gaia DR2 3189152962633165056, Gaia DR3 3189152962633165056 |