The Eskimo Nebula is a bipolar planetary nebula located in Gemini constellation. It is sometimes also known as the Clown Face Nebula. The nebula has the designation NGC 2392 in the New General Catalogue. It got the nickname Eskimo because its shape resembles a head wearing a fur-lined parka hood.
With an apparent magnitude of 10.1, the nebula is invisible to the unaided eye, but can be seen in a small telescope. It is, however, best viewed with a larger telescope, which reveals some of the nebula’s details.
The Eskimo Nebula lies at a distance of over 2,870 light years from Earth. It was created roughly 10,000 years ago, when a Sun-like star used up all the hydrogen at its core, started to cool and expand, growing by tens to hundreds of times its original size, and eventually expelled its outer layers to form the planetary nebula. The central star will eventually collapse and become a white dwarf.
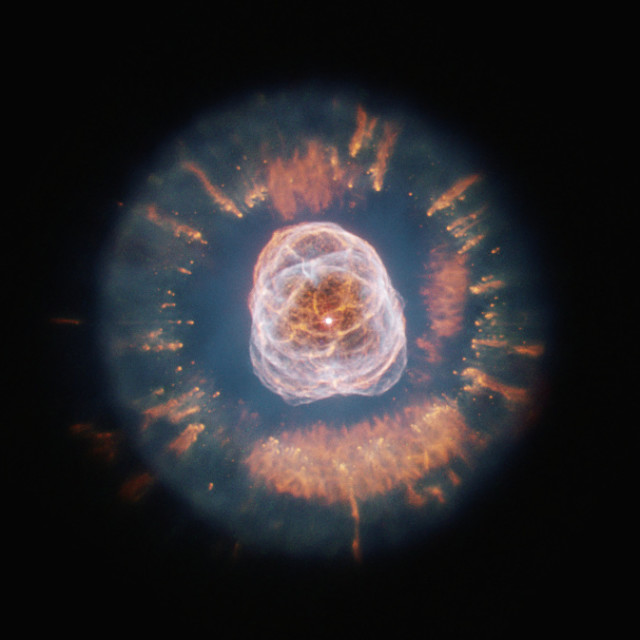
Eskimo Nebula (NGC 2392). Image: Judy Schmidt
The radiation of the star’s hot core and interaction of stellar winds have created the nebula’s expanding shell. The Eskimo Nebula spans about a third of a light year and is located in our galaxy, the Milky Way.
The nebula is composed of two elliptical lobes of matter that trail above and below the central star. What appears as a furred parka to observers is really a disk of material containing a number of comet-shaped objects appearing to move away from the nebula’s central star.
The Eskimo’s face is really a bubble of material blown into space by the star’s strong stellar winds.
The Eskimo Nebula can be found halfway between the stars Kappa and Lambda Geminorum, near the 4th magnitude star Wasat (Delta Geminorum). In small telescopes, the nebula appears as a star surrounded by a faint haze. In larger telescopes, the central star is seen shining though a diffuse shell of gas, slightly green in colour.
Facts
The Eskimo Nebula was discovered by the the German-born British astronomer William Herschel on January 17, 1787. Viewing the object from Slough, England, Herschel described it as, a “star 9th magnitude with a pretty bright middle, nebulosity equally dispersed all around. A very remarkable phenomenon.”
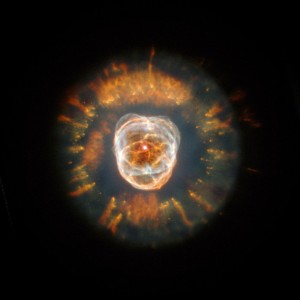
Eskimo nebula (NGC 2392). In its first glimpse of the heavens following the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a majestic view of a planetary nebula, the glowing remains of a Sun-like star in its final stages. This stellar relic, first spied by William Herschel in 1787, is nicknamed the “Eskimo” Nebula (NGC 2392) because, when viewed through ground-based telescopes, it resembles a face surrounded by a fur parka. In this Hubble telescope image, the “parka” is really a disk of material embellished with a ring of comet-shaped objects, with their tails moving away from the central star. The Eskimo’s “face” also contains some fascinating details. Although this bright central region resembles a ball of twine, it is, in reality, a bubble of material being blown into space by the central star’s intense “wind” of high-speed material. In this photo, one bubble lies in front of the other, obscuring part of the second lobe. Scientists believe that a ring of dense material around the star’s equator, ejected during its red giant phase, created the nebula’s shape. The bubbles are not smooth like balloons but have filaments of denser matter. Each bubble is about 1 light-year long and about half a light-year wide. Scientists are still puzzled about the origin of the comet-shaped features in the “parka.” One possible explanation is that these objects formed from a collision of slow-and fast-moving gases. The Eskimo Nebula is about 5,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Gemini. The picture was taken Jan. 10 and 11, 2000, with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. The nebula’s glowing gases produce the colors in this image: nitrogen (red), hydrogen (green), oxygen (blue), and helium (violet). Image: NASA, ESA, Andrew Fruchter (STScI), and the ERO team (STScI + ST-ECF).
The Eskimo Nebula is one of the youngest planetary nebulae known. It started forming only about 10,000 years ago, when the central star started ejecting material into space. Scientists believe that the star had a ring of dense material around the equator, which was ejected during the star’s red giant phase. The equatorial disk was responsible for creating the nebula’s shape.
Scientists observed the nebula as part of a study of three planetary nebulae with hot gas in their central region. The study was published in April 2013. NGC 2392 had significantly higher levels of X-ray emission compared to the other two nebulae, which indicates that the hot central star has an unseen companion.
The other two nebulae studied – the Spirograph Nebula (IC 418) in Lepus constellation and the Blinking Planetary Nebula (NGC 6826) in Cygnus – had fainter X-ray emissions, probably produced by shock fronts in the stellar wind emanating from the central star.
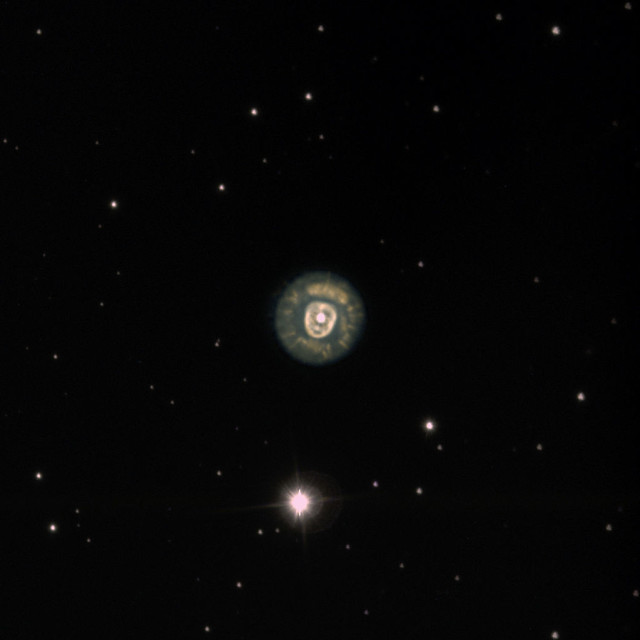

NGC 2392 (the Eskimo nebula) is a small planetary nebula in the constellation of Gemini. This false-color image is a digital composite made from images taken at the Vatican Advanced Technology Telescope (VATT) telescope on Mt. Graham. Image: Vatican Observatory
Eskimo Nebula – NGC 2392
Constellation: Gemini
Coordinates: 07h 29m 10.7669s (right ascension), +20°54’42.488” (declination)
Distance: ≥ 2,870 light years (≥ 880 parsecs)
Radius: ≥ 0.34 light years
Visual magnitude: 10.1
Absolute magnitude: ≤0.4
Apparent dimensions: 48″ × 48″
Age: 10,000 years
Designations: Eskimo Nebula, Clown Face Nebula, Clown Face, NGC 2392, Caldwell 39, HIP 36369,
BD+21 1609, PN G197.8+17.3