The Fish Head Nebula is an emission nebula located approximately 6,000 light-years away in the northern constellation Cassiopeia. The nebula is 3.1 arcminutes across and appears adjacent to the larger and better-known Heart Nebula (Sharpless 2-190). It is catalogued as IC 1795 in the Index Catalogue.
The Fish Head Nebula is a popular target for astrophotographers, not only for its fish-like appearance, but also because it appears in the region of the larger and better-known Heart and Soul Nebulae in Cassiopeia. IC 1795 is an extension of the much larger Heart Nebula (Sharpless 2-190), which stretches across 150 arcminutes and forms a pair with the neighbouring Soul Nebula (Sharpless 2-199).
IC 1795 has been nicknamed the Fish Head Nebula because its shape resembles that of the head of a fish. It is sometimes also known as the Northern Bear Nebula. The nebula is part of a huge star forming region excited by the light of newly formed stars. The large stellar nursery includes the neighbouring Heart and Soul Nebulae. The three nebulae appear at the edge of a vast molecular cloud.
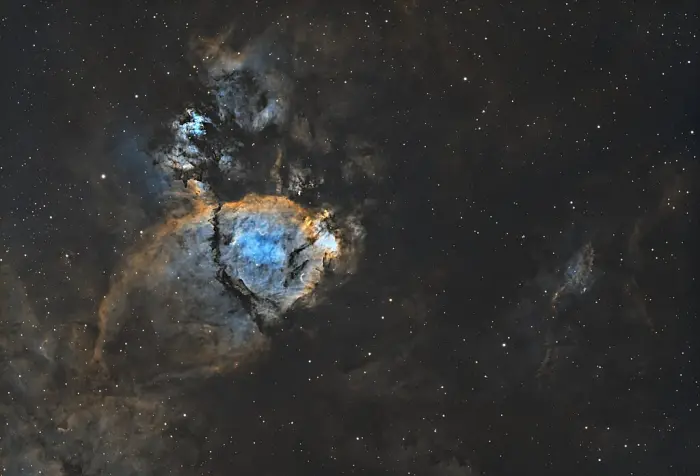

The Fish Head Nebula (IC 1795), image credit: Wikimedia Commons/Astrophoto Andy (CC0 1.0)
The brightest portion of the Fish Head Nebula is listed as NGC 896 in the New General Catalogue. NGC 896 is a relatively bright knot that appears on the western side of IC 1795. It contains numerous young massive stars. The luminous stars emit high amounts of ultraviolet light that excites the nebular gas, causing it to glow.
The brightest stars in the region of the Fish Nebula are hot, luminous O- and B-type stars. These are among the most massive and luminous type of stars in the universe. They are also the shortest-lived stars because they burn through their supply of hydrogen quickly due to their high mass.
NGC 896 is also the brightest part of the larger Heart Nebula. The Heart Nebula has a radius of 165 light-years. Even though it occupies more than 2 degrees in the sky (four times the diameter of the full Moon), it has a low surface brightness and is a challenging target in small telescopes and in less than ideal conditions. The emission nebula has an apparent magnitude of 18.3.
The dark nebula that appears next to the Fish Head is catalogued as LDN 1359.
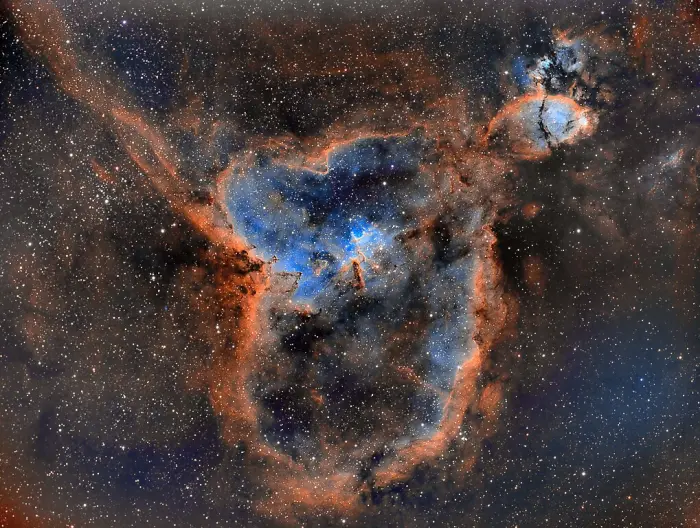

The Heart Nebula region is about 7500 light years away from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The 330 light year diameter complex contains the eponymous emission nebula (Ced7/Cr26/IC1805/LBN654/Mel15/Sh2-190) shaped correspondingly, along with a separate region labelled the Fish Head Nebula (Ced6/IC1795/LBN645/NGC896), which was the first part to be discovered. Image credit: Ram Samudrala (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
NGC 896, the brighter part of the Fish Head Nebula, was discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel on November 3, 1787. Faint nebulae were difficult targets for the telescopes used at the time, so the rest of the Fish Head was not spotted until a full century later.
The entire Fish Head Nebula (IC 1795) was discovered by the American astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard in the late 1890s. Barnard also discovered the neighbouring Heart and Soul Nebulae (Sharpless 2-190 and Sharpless 2-199).
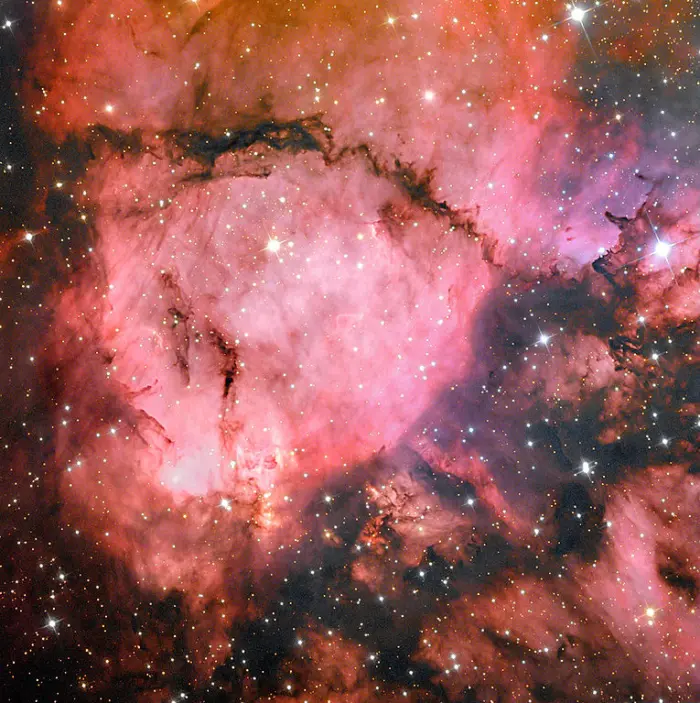

NGC 896 in the Fish Head Nebula, image credit: Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona (CC BY-SA 4.0)
Location
The Fish Head Nebula lies in the eastern part of the constellation Cassiopeia, near the border with Perseus. It can be found using the bright stars of Cassiopeia’s W. These are Schedar (Alpha Cassiopeiae), Caph (Beta Cassiopeiae), Gamma Cassiopeiae, Ruchbah (Delta Cassiopeiae), and Segin (Epsilon Cassiopeiae).
The Fish Head Nebula lies in the region between Segin, the leftmost star of the W, and Miram (Eta Persei), one of the relatively bright stars that form the Segment of Perseus. The Segment of Perseus is a prominent curved line of stars in the area between Cassiopeia’s W, the bright Capella in Auriga, and the brightest stars of Andromeda (Alpheratz, Mirach, and Almach). The Heart, Soul and Fish Head nebulae lie northeast of the Double Cluster, an open cluster visible to the unaided eye on a clear night.
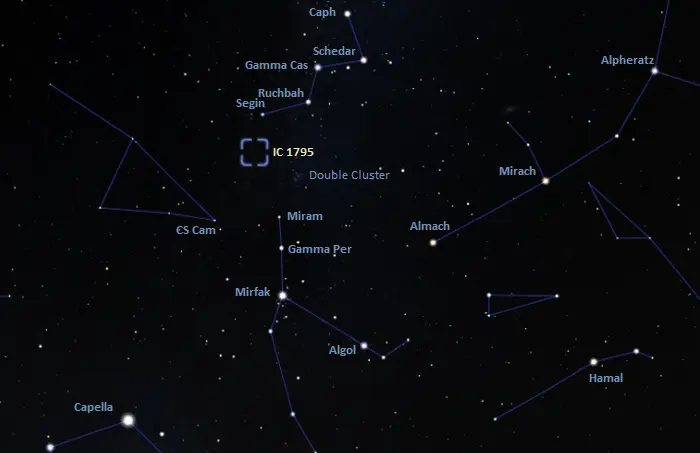
The location of the Fish Head Nebula, image: Stellarium
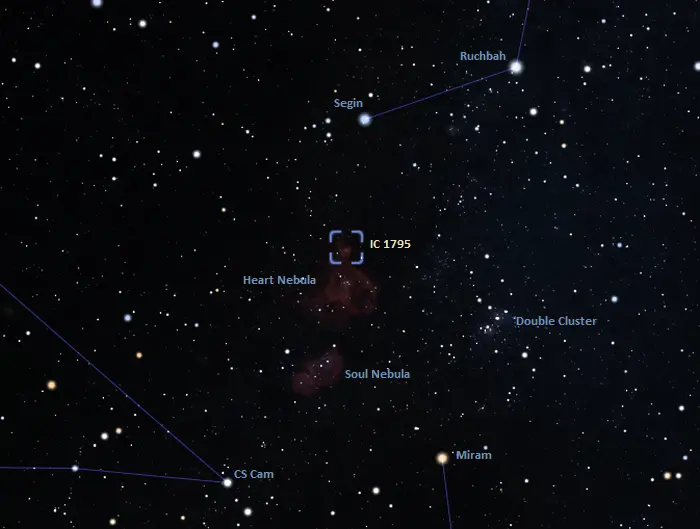
Fish Head Nebula finder chart, image: Stellarium
The best time of the year to see the Fish Head Nebula and other deep sky objects in Cassiopeia is during the month of November, when the constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening.
At declination +62° 02′, the Fish Head Nebula is visible from locations north of the latitude 28° S.
Fish Head Nebula – IC 1795
| Constellation | Cassiopeia |
| Object type | H II region |
| Right ascension | 02h 26m |
| Declination | +62° 02′ |
| Apparent size | 3’.1 x 3’.1 |
| Distance | 6,000 light-years (1,839 parsecs) |
| Names and designations | Fish Head Nebula, Northern Bear Nebula, IC 1795, NGC 896, CTB 9, LBN 645, LBN 133.80+01.10, GAL 133.70+01.20, GAL 133.71+01.21, GAL 133.72+01.21 |
Images
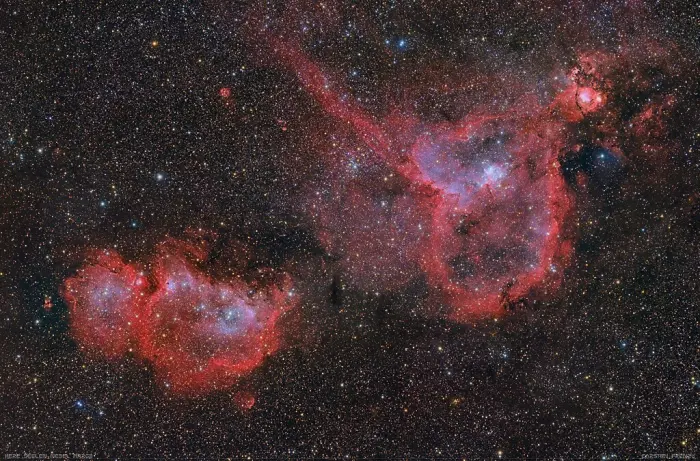

Heart and Soul nebulae with the Fish Head Nebula (right), image credit: Carsten Frenzl (CC BY 2.0)
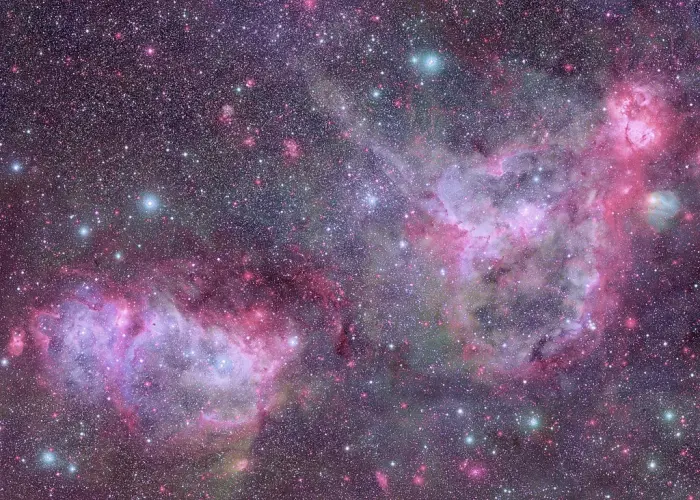

The Soul Nebula (left) and the Heart Nebula (right), image credit: Giuseppe Donatiello (CC0 1.0)
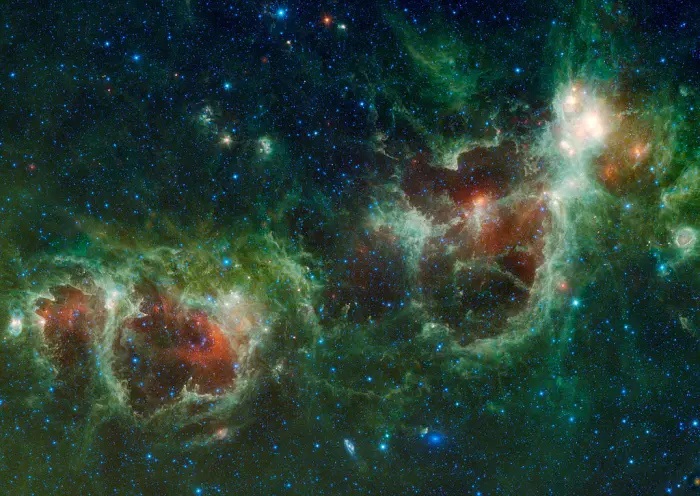

The Heart and Soul nebulae are seen in this infrared mosaic from NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. The Fish Head Nebula appears in the top right corner. Also visible near the bottom of this image are two galaxies, Maffei 1 and Maffei 2. Maffei 1 is the bluish elliptical object and Maffei 2 is the spiral galaxy. All four infra-red detectors aboard WISE were used to make this image. Colour is representational: blue and cyan represent infra-red light at wavelengths of 3.4 and 4.6 microns, which is dominated by light from stars. Green and red represent light at 12 and 22 microns, which is mostly light from warm dust. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA (PD)
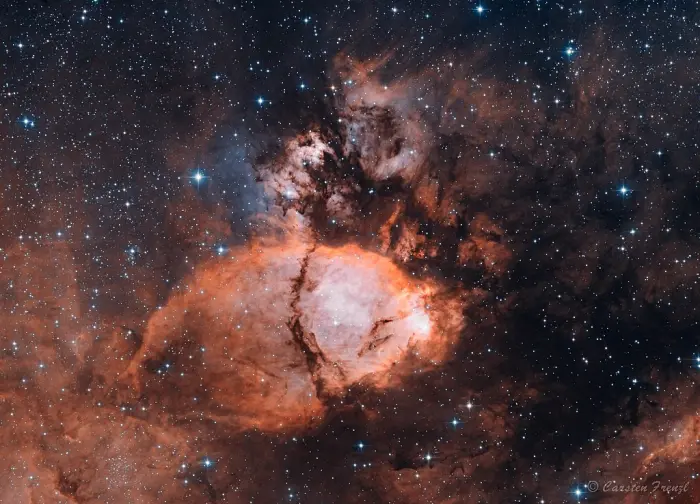

The Fish Head Nebula (IC 1795), image credit: Carsten Frenzl (CC BY 2.0)
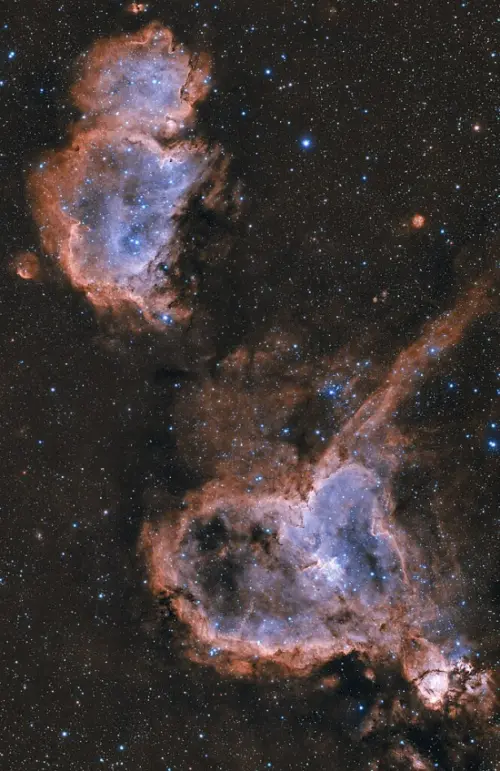

Heart and Soul Nebula and the Fish Head Nebula (bottom right corner), image credit: Wikimedia Commons/Nielander (CC0 1.0)