The Little Sombrero Galaxy is a spiral galaxy located approximately 40 million light years away in the northern constellation Pegasus. With an apparent magnitude of 11.6 and an apparent size of 5.5 by 2.3 arcminutes, it can be observed in amateur telescopes. It is listed as NGC 7814 in the New General Catalogue and Caldwell 43 (C43) in the Caldwell catalogue.
NGC 7814 appears edge-on when seen from Earth. It has a diameter of about 80,000 light years. The galaxy was named the Little Sombrero because of its resemblance to the brighter Sombrero Galaxy (Messier 104), located in the constellation Virgo, near the border with Corvus.
Like the Sombrero Galaxy, NGC 7814 has a bright central bulge, a dark, narrow dust band obscuring its nucleus, and a bright halo of stars and glowing gas extending outwards. However, unlike the Sombrero, it appears almost exactly edge-on.
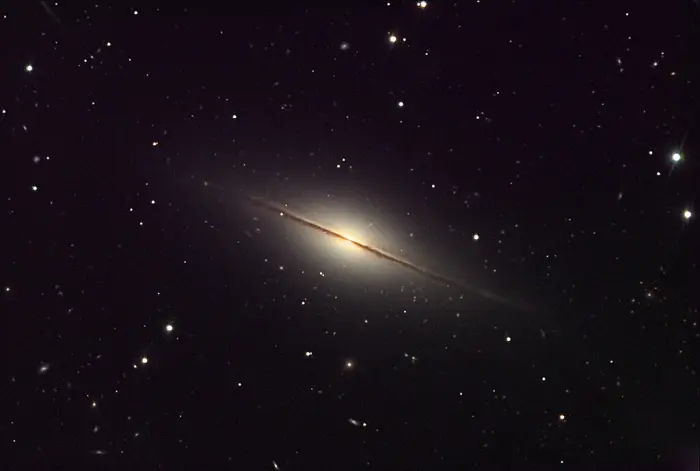

The Little Sombrero Galaxy (NGC 7814). The background dust lanes can be seen “above” and through the halo, giving this galaxy more depth than is usually displayed. This image was taken as part of Advanced Observing Program (AOP) program at Kitt Peak Visitor Center during 2014. Image credit: KPNO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/Adam Block (CC BY 4.0)
The Little Sombrero Galaxy has a slightly warped galactic plane. It is one of the few galaxies that show this feature in optical wavelengths.
The galaxy is the most prominent member of the NGC 7814 Group of galaxies. The group includes the fainter irregular galaxy NGC 14 and the dwarf galaxy UGC 17.

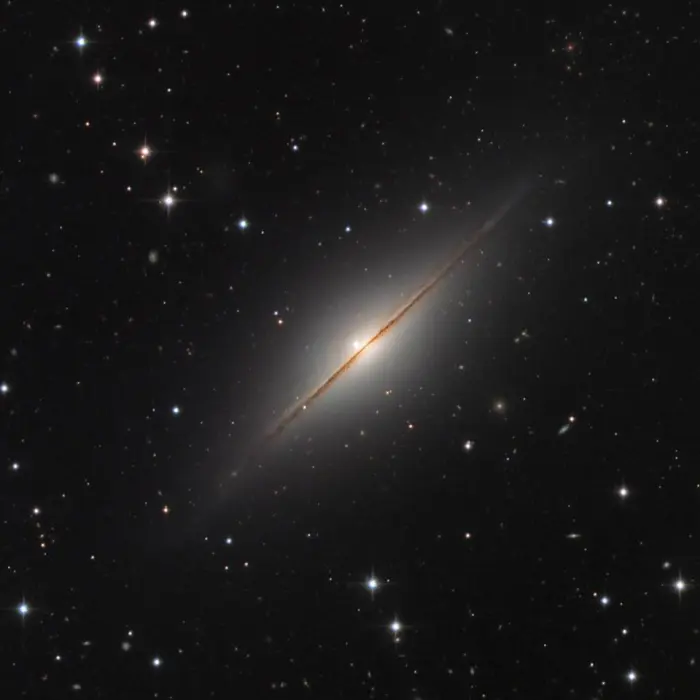
Hubble has allowed astronomers to view galaxies of all shapes and sizes from nearly every angle. When a galaxy is seen edge-on, the mesmerizing perspective reveals a dazzling slice of the universe. Caldwell 43, also known as the “Little Sombrero,” is one such galaxy. This image of Caldwell 43 is a combination of visible and infrared observations captured by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys in 2006. The observations were taken to assist astronomers in studying the galaxy’s stellar populations, and to help shed light on the evolution of this galaxy and others like it. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA; Acknowledgment: Josh Barrington (CC BY 2.0)
Facts
The Little Sombrero Galaxy was discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7-inch reflector on October 8, 1784. This was only three years after the French astronomer Pierre Méchain found the brighter Sombrero Galaxy (M104). Herschel listed the galaxy as II 240 in his catalogue, describing the object as “pretty faint, pretty large, irregularly round, easily resolvable.”
The Danish astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer, who compiled the New General Catalogue, described NGC 7814 as “considerably bright, considerably large, extended, very gradually brighter middle.”
The Little Sombrero appears in a star field rich with faint background galaxies, revealed by images captured with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The light from these remote galaxies becomes redder (dimmer) as it passes through the Little Sombrero’s halo. Astronomers have used this to measure the amount of dust and gas in the galaxy’s halo.
A supernova was detected in the galaxy in 2021. Designated SN 2021rhu, it was classified as a Type Ia supernova. At the time of discovery, it had an apparent magnitude of 15.11.
The brighter Sombrero Galaxy in the constellation Virgo has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.0 and an apparent size of 9 by 4 arcminutes. It appears brighter and larger than the Little Sombrero because it lies much closer to us, at a distance of 31.1 million light years. The two galaxies are in fact almost the same size.

The Little Sombrero Galaxy by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), image credit: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (CC BY 2.5)
Location
The Little Sombrero Galaxy lies in the region of the Great Square of Pegasus, a prominent asterism formed by the Pegasus stars Scheat (Beta Pegasi), Markab (Alpha Pegasi), and Algenib (Gamma Pegasi) with Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae) in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy appears near Algenib, the faintest of the four stars. It can be spotted with 7-inch and larger telescopes. At declination +16°, it is visible from locations north of the latitude 74° S.
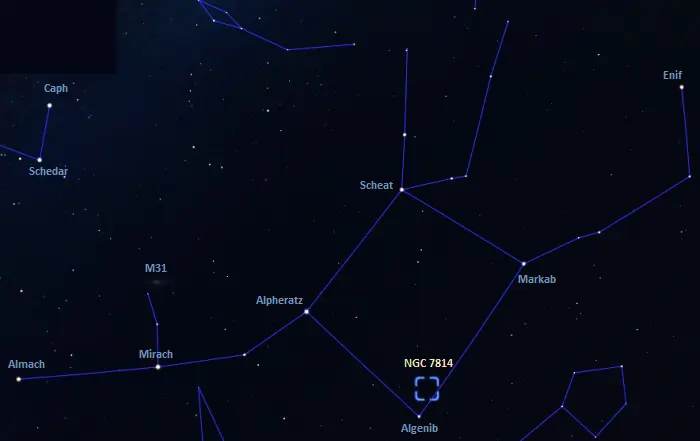
The location of the Little Sombrero Galaxy (NGC 7814), image: Stellarium
A fainter galaxy, IC 5381, appears only 10 arcminutes south of the Little Sombrero. It was discovered by the British amateur astronomer and astrophotography pioneer Isaac Roberts photographically in 1895, a full century after the discovery of NGC 7814. The galaxy lies much farther away and is not related to the Little Sombrero.
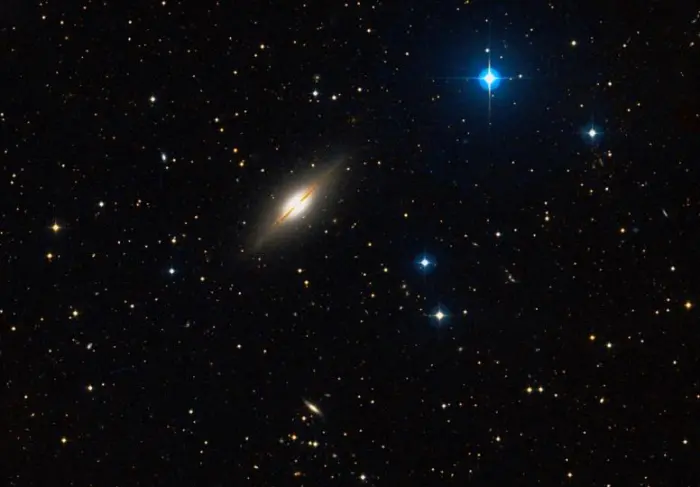

IC 5381 below the brighter Little Sombrero Galaxy (NGC 7814), image: Wikisky (DSS2)
The best time of the year to observe The Little Sombrero Galaxy and other deep sky objects in Pegasus is during the month of October, when the constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening.
Little Sombrero Galaxy – NGC 7814
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Object type | Spiral galaxy |
| Morphological type | SA(S)ab |
| Right ascension | 00h 03m 14.947s |
| Declination | +16° 08′ 42.82″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 11.6 |
| Apparent size | 5.5′ × 2.3′ |
| Distance | 40.0 ± 2.6 million light-years (12.2 ± 0.8 megaparsecs) |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 1,048 ± 3 km/s |
| Names and designations | Little Sombrero Galaxy, NGC 7814, Caldwell 43, C43, UGC 8, PGC 218, LEDA 218, MCG+03-01-020, KUG 0000+158, IRAS F00006+1552, 2MASX J00031494+1608428, ISOSS J00032+1608, LAMOST J000314.92+160843.0, Z 456-24, Z 0000.7+1552, UZC J000314.9+160843 |