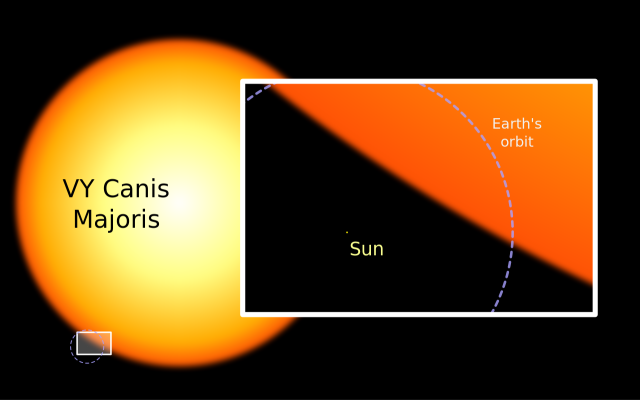
VY Canis Majoris (VY CMa) is an exceptionally large, luminous red hypergiant star located in the constellation Canis Major.
With a radius about 1,420 times that of the Sun, corresponding to a diameter of 13.2 astronomical units, VY Canis Majoris is one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way. The star lies at an approximate distance of 3,840 light years from Earth and has an apparent magnitude that varies from 6.5 to 9.6. It is classified as a semiregular variable star and has an estimated period of 2,000 days.
Hypergiants are stars with enormous luminosity that lose mass at a very high rate. With an estimated luminosity about 270,000 times that of the Sun, VY Canis Majoris is one of the most luminous members of its class.
The star is losing an enormous amount of mass – about 30 times the mass of the Earth every year – as it enters the final stage of its life before going out as a supernova. The cloud of expelled material – dust and gas – is pushed away by the star’s radiation pressure and it keeps moving outwards.
The dust and gas expelled by VY Canis Majoris will eventually be used by new stars, along with the heavier elements left behind by the supernova, possibly to form planets.
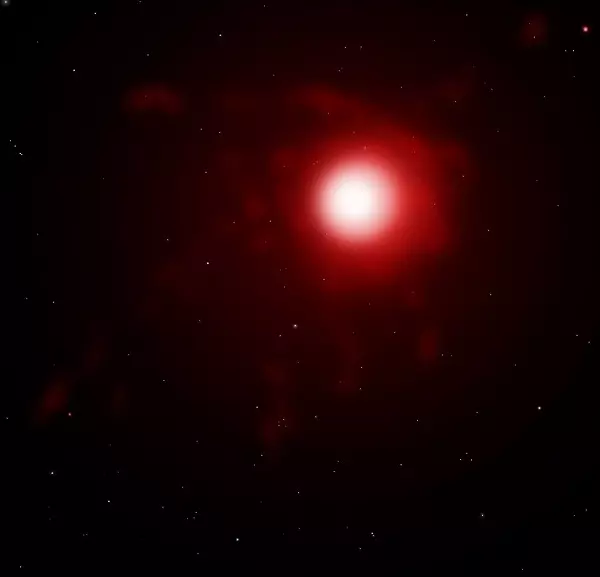

VY Canis Majoris. Image: Wikimedia Commons/Sephirohq
Facts
VY Canis Majoris was first catalogued by the French astronomer Jérôme Lalande on March 7, 1801. Lalande listed it as a 7th magnitude star.
Other 19th century observations revealed that the star has been fading since 1850. At the time, VY Canis Majoris was suspected to be a multiple star, but now the components that were detected by 19th century observers are known to be bright patches in the nebula surrounding the star. VY Canis Majoris was confirmed not to have any companions by visual observations in 1957 and imaging in 1998.
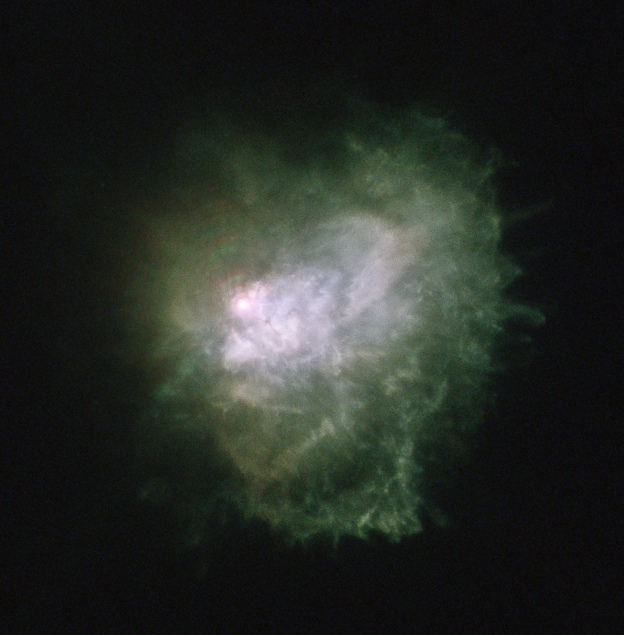
VY Canis Majoris ejecta shell. Image: Judy Schmidt
The star’s properties indicate that it was an O-type star with an estimated mass between 15 and 35 times that of the Sun during its main sequence.
Size
The diameter of VY CMa, 13.2 astronomical units, corresponds to about 1,976,640,000 kilometres. While different sources give different estimates of the hypergiant’s radius, if it were placed at the centre of our solar system, the star’s surface would extend well beyond the orbit of Jupiter.
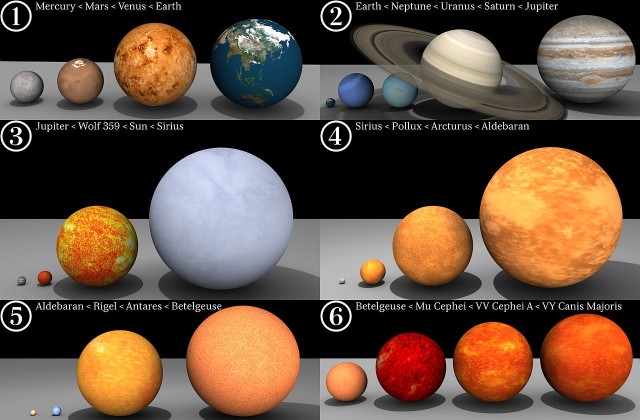

VY Canis Majoris compared to other large stars. Relative sizes of the planets in the solar system and several well known stars. Star colours are estimated (based on temperature) and Saturn’s rings are shown slightly larger in the picture than to scale. Blender 3D was used for the models, lighting, and rendering. The GIMP was used to assemble and label the six renders into a single image. Wolfram Alpha was used to calculate each star’s base colour through Wien’s Law. The relative sizes of stars in terms of their representative solar radius were calculated for all stars in each frame. Texture maps for stars were created using images of the Sun from SOHO. Planetary texture and bump maps (excluding Earth) were from Celestia Motherlode. Lastly, Earth’s texture and bump map were obtained from Natural Earth III. Image: Dave Jarvis
Astronomers originally estimated the star’s radius at 1,800 to 2,100 solar radii, which made VY CMa the largest star known at the time. More recent estimates give it a radius of about 1,420 solar radii. This still makes VY CMa considerably larger than Betelgeuse, which has a radius about 1,180 times solar, Antares, estimated to be 883 times larger than the Sun, and many other known large stars.
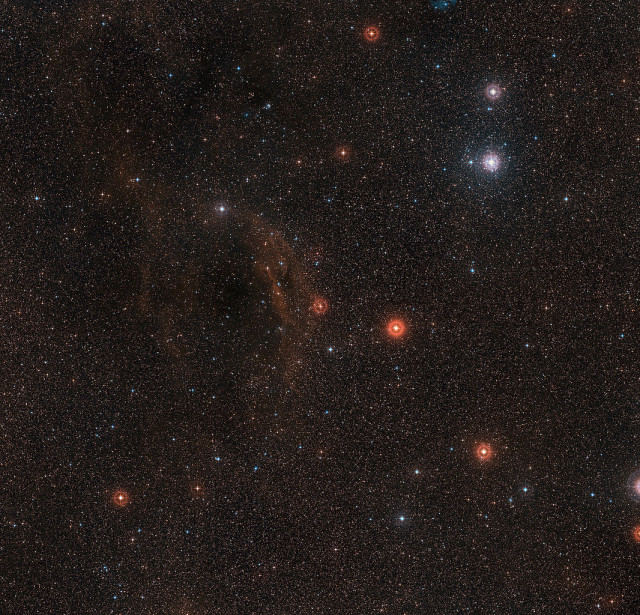

This wide-field view shows the sky around the very brilliant red hypergiant star VY Canis Majoris, one of the largest stars known in the Milky Way. The star itself appears at the centre of the picture, which also includes clouds of glowing red hydrogen gas, dust clouds and the bright star cluster around the bright star Tau Canis Majoris towards the upper right. Image: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2. Acknowledgement: Davide De Martin, November 2015
It is, however, smaller than VX Sagittarii, an evolved red supergiant in Sagittarius (1,520 solar radii), Westerlund 1-26 (1,530), a red supergiant or hypergiant located in Ara constellation, WOH G64 (1,540 – 1,730), a red hypergiant located in the Large Magellanic Cloud in Dorado, the orange hypergiant RW Cephei (1,636) in Cepheus, the red hypergiant NML Cygni (1,642 – 2,775) in Cygnus, and the red supergiant UY Scuti (1,708), located in the constellation Scutum.
VY Canis Majoris compared to the Sun
Hypernova
VY Canis Majoris is large enough to produce a hypernova, or superluminous supernova. Hypernovae produce a considerably higher amount of energy than regular supernovae, as well as long-duration gamma ray bursts, which are among the most energetic events observed in the universe.
When VY CMa reaches the end of its life cycle, it may release more energy than 100 standard supernovae, as well as enormous quantities of gamma rays. Being almost 4,000 light years away, the star is too distant from Earth for the supernova to affect us, but a hypernova event would almost certainly destroy any life on any planets in its range.
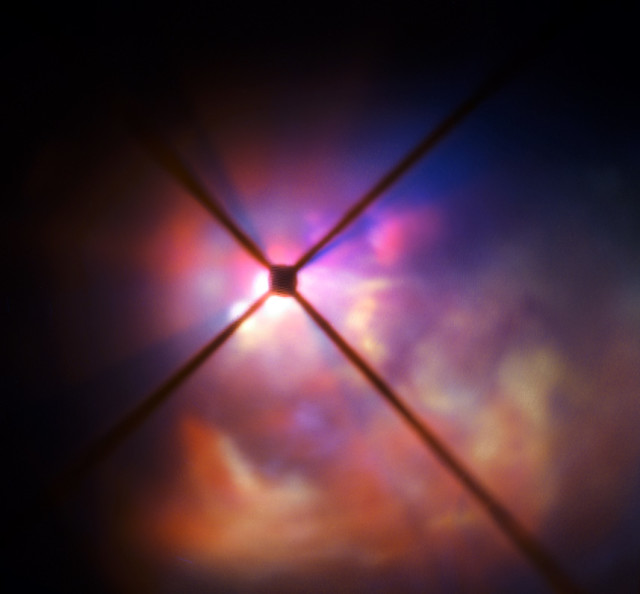

The star VY Canis Majoris is a red hypergiant, one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way. It is 30–40 times the mass of the Sun and 300 000 times more luminous. In its current state, the star would encompass the orbit of Jupiter, having expanded tremendously as it enters the final stages of its life. New observations of the star using the SPHERE instrument on the VLT have clearly revealed how the brilliant light of VY Canis Majoris lights up the clouds of material surrounding it and have allowed the properties of the component dust grains to be determined better than ever before. In this very close-up view from SPHERE the star itself is hidden behind an obscuring disc. The crosses are artefacts due to features in the instrument. Image: ESO, November 2015
VY Canis Majoris
Constellation: Canis Major
Right ascension: 07h 22m 58.32877s
Declination: −25° 46′ 03.2355″
Spectral class: (M2.5I-)M3-M4.5
Apparent magnitude: 6.5 to 9.6 (7.9607)
Distance: 3,840 light years (1,170 parsecs)
Variable type: semiregular
Mass: 30 to 40 solar masses
Radius: 1,420 ± 120 solar radii
Luminosity: 270,000 solar luminosities
Temperature: 3,490 K
Radial velocity: 41 km/s
Designations: VY Canis Majoris, VY CMa, HD 58061, CD -25 4441, HIP 35793, AAVSO 0718-25
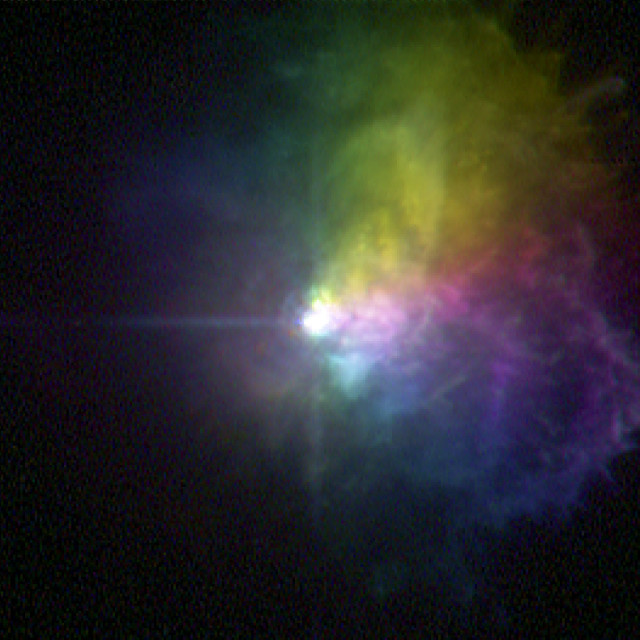

Using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the W.M. Keck Observatory, Kameula, Hawaii, astronomers have learned that the gaseous outflow from one of the brightest super-sized stars in the sky is more complex than originally thought. The outbursts are from VY Canis Majoris, a red supergiant star that is also classified as a hypergiant because of its very high luminosity. The eruptions have formed loops, arcs, and knots of material moving at various speeds and in many different directions. The star has had many outbursts over the past 1,000 years as it nears the end of its life. Image: NASA, ESA, and R. Humphreys (University of Minnesota), 2007